Table of Contents
Capturing process data
These instructions describe the “step by step” procedure to write process data based on definable triggers into a database.
In tutorial a SIMATIC S7 PLC is used as data source and a local SQLite Database as data target.
As Codabix offers a uniform interface that is used to access connected devices and databases, this procedure is applicable to any type of data,
that is defined in Codabix.
Requirements
System requirements
To carry out the following steps you need a computer (running Windows or Linux), on which you have the necessary rights to install applications.
Furthermore, an internet connection in necessary to load Codabix and the provided standard configuration and to be able to access sample data from our publicly available SIMATIC S7 PLC.
The exact system requirements for hardware and operating system version can be found here:
Required plugins
The following Codabix plugins are required
- S7 Device Plugin: Connection to the SIMATIC S7 PLC
- Script Interface Plugin: Processing the triggers and transferring the data
1. Step: Setting up Codabix
In this step you install Codabix on your system.
For the purpose of this tutorial we provide you with a basic configuration
for the process data acquisition.
1.1 Installation
- Download in the Download area the current version of Codabix (these instructions require at least v1.4.0) for the system, where your want to run Codabix.
- After a successful download, install Codabix on your system and follow the steps for the first start:
1.2 Configuration
- Download the following default configuration: capture-process-data_default_2023-07-28.cbx
- Import the configuration into Codabix
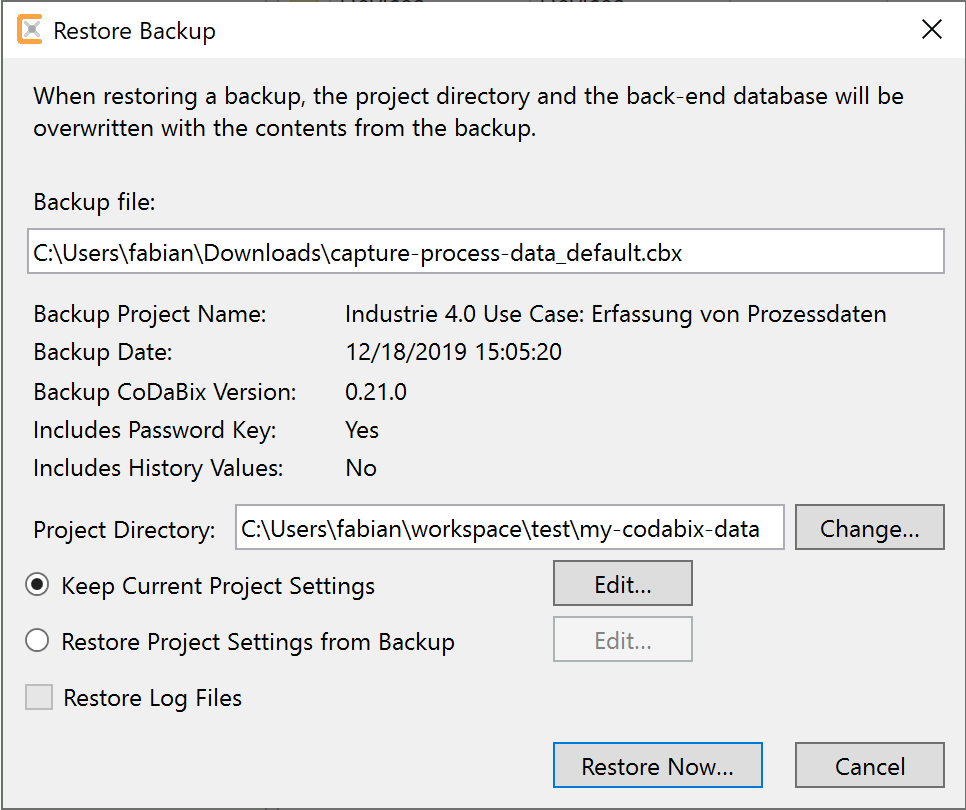
- For Codabix v1.0.0 and above (including the preview versions) it is now possible to restore a backup via the web configuration:
- Open the Codabix web configuration in a browser as described here
- Click on the sidebar menu entry Backup & Restore
- In the section Restore Backup click on the button Select Backup file…
- In the Open File dialog: Select the default configuration file you downloaded in the previous step
- After uploading the file to the server click the button Restore Now… to restore the backup
- Alternatively, you can restore the backup in the Codabix application:
- Windows
- Click
 on the right side of the taskbar
on the right side of the taskbar
- Linux/Raspberry Pi/Siemens IOT2050
- Select the menu item
4) Restore Backupin the console application - Enter the path to the loaded file and start the import by pressing the
Enter-key
- Docker
- The procedure for restoring a backup within a Docker container can be found in the associated Github repository: https://github.com/Traeger-GmbH/codabix-docker#restoring-from-a-backup-file
2. Step: Setting up the process data acquisition
In this example, the values of two variables (Duration and Quantity) will be read from the PLC and a new entry will be created in a database table,
which also contains the MachineID and the current timestamp. The MachineID can be used to associate the database entry with the source PLC.
This process should be carried out when the rising edge of the JobCompleted bit is detected in the PLC.
The PLC variables are defined as follows:
Process data
Duration- Datatype: Real
- Address: DB511.DBD 0
Quantity- Datatype: DInt
- Address: DB511.DBD 4
Trigger
JobCompleted- Datatype: Bit
- Address: DB511.DBX 10.0
The database table named oeemachinerecord has the following columns:
ID- Datatype: INT
MachineID- Datatype: INT
Duration- Datatype: Double
Quantity- Datatype: INT
Timestamp- Datatype: DATETIME
In order to map the data acquisition (henceforth referred to as Transfer) in Codabix, it is divided into three components:
- Inputs: Variables whose values are to be recorded
- Outputs: Variables in which the data to be recorded will be saved
- Triggers: Variables that trigger a data transfer from the Inputs to the Outputs
These components are mapped using a folder structure within Codabix.
Each folder that is located under the path /Nodes/Transfers represents an independent transfer.
2.1 Creating a new transfer
To create a new transfer, navigate to the /Nodes/Transfers node in the node tree.
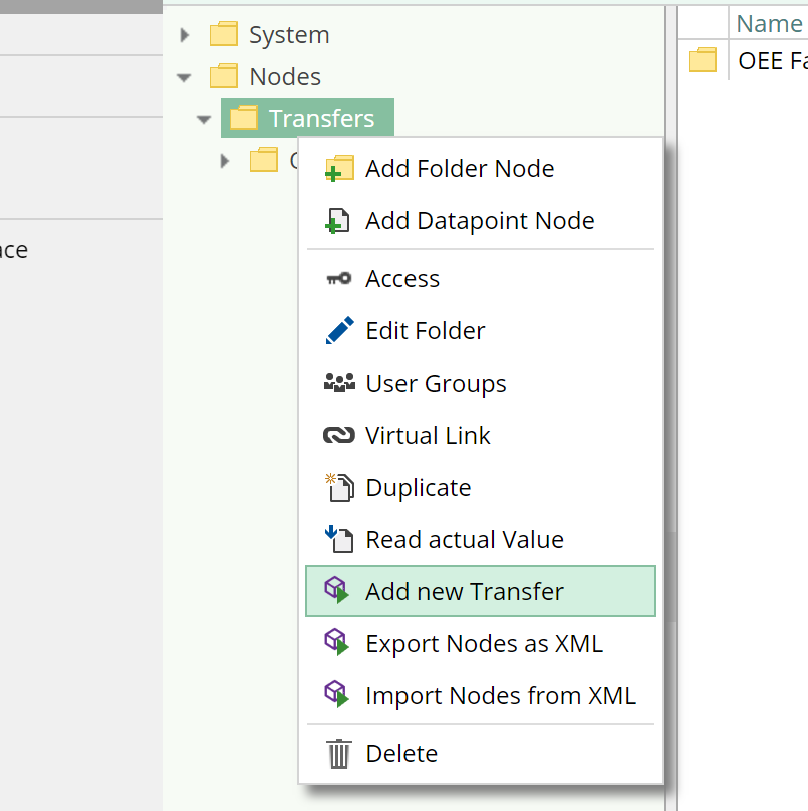
- Create a new transfer:
- Right click on the node
/Nodes/Transfers
- Name the new transfer:
- Right click on the new node
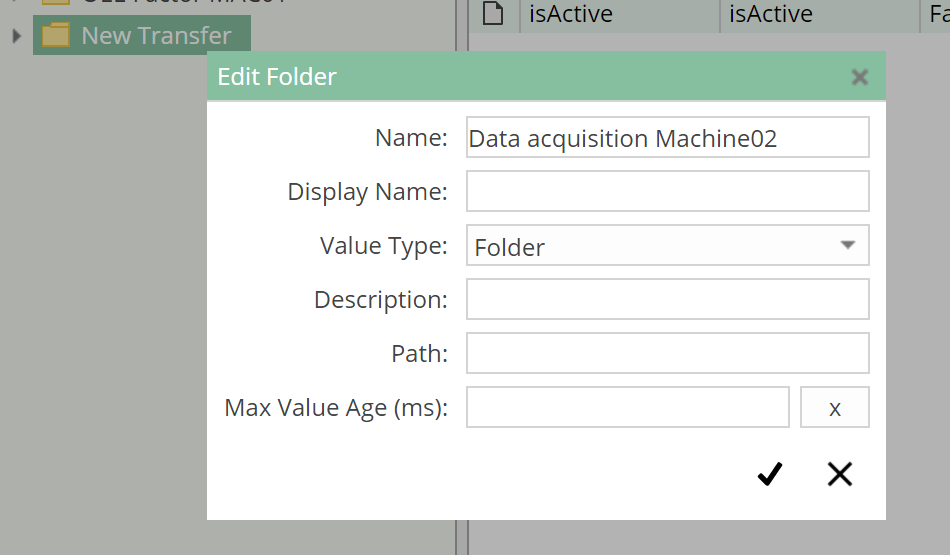
New Transfer - Click on the context menu entry
Edit Folder - In the
Edit Folderdialog, change the name toData acquisition Machine02
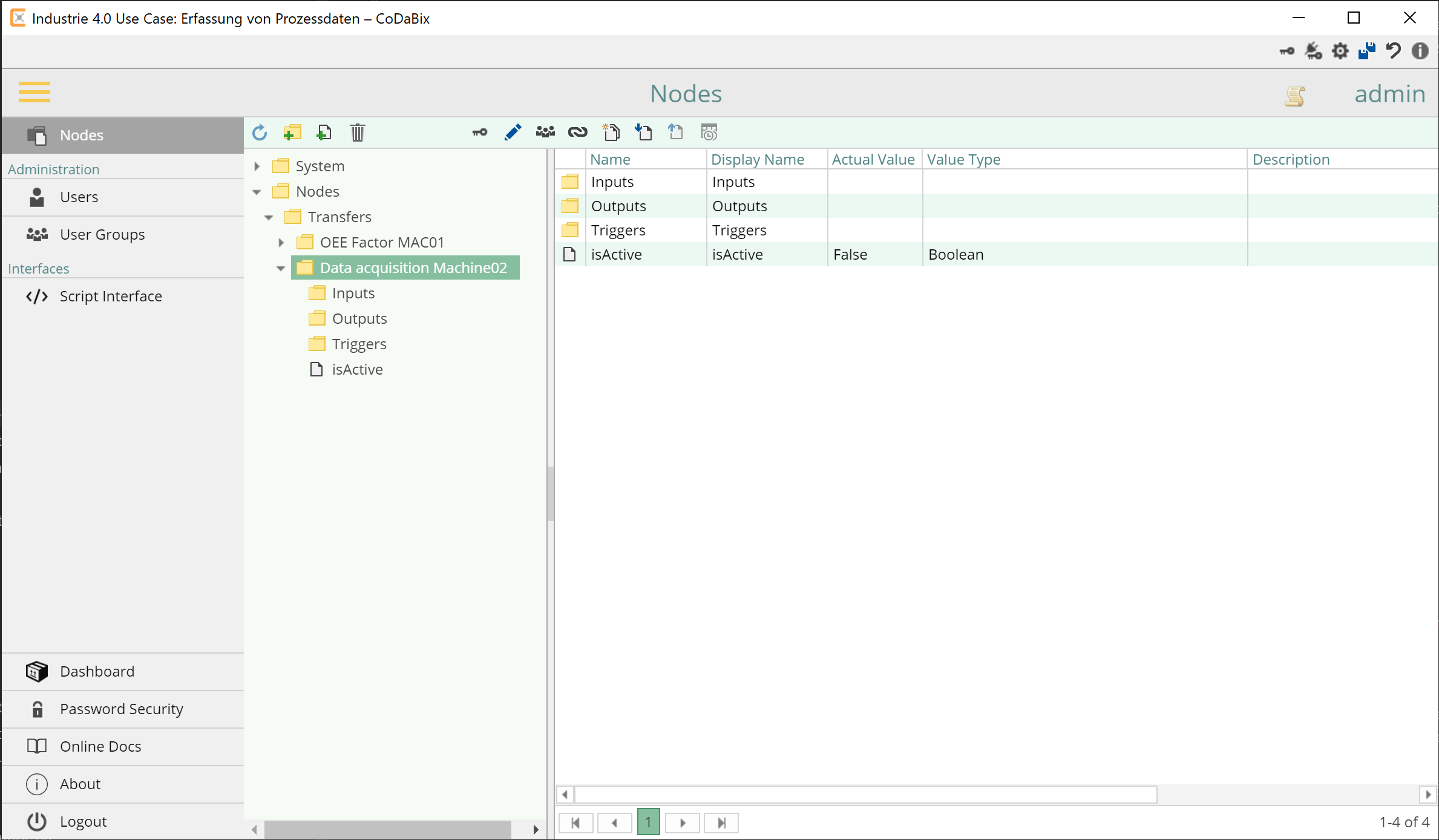
The node tree should then look like this:
2.2 Selection of the data to be recorded
In order to define variables whose values are to be recorded, these varibles must be located under the folder node Inputs.
In addition to the variables from the PLC, the ID of the machine (for this example MachineID = 2) shall be recorded.
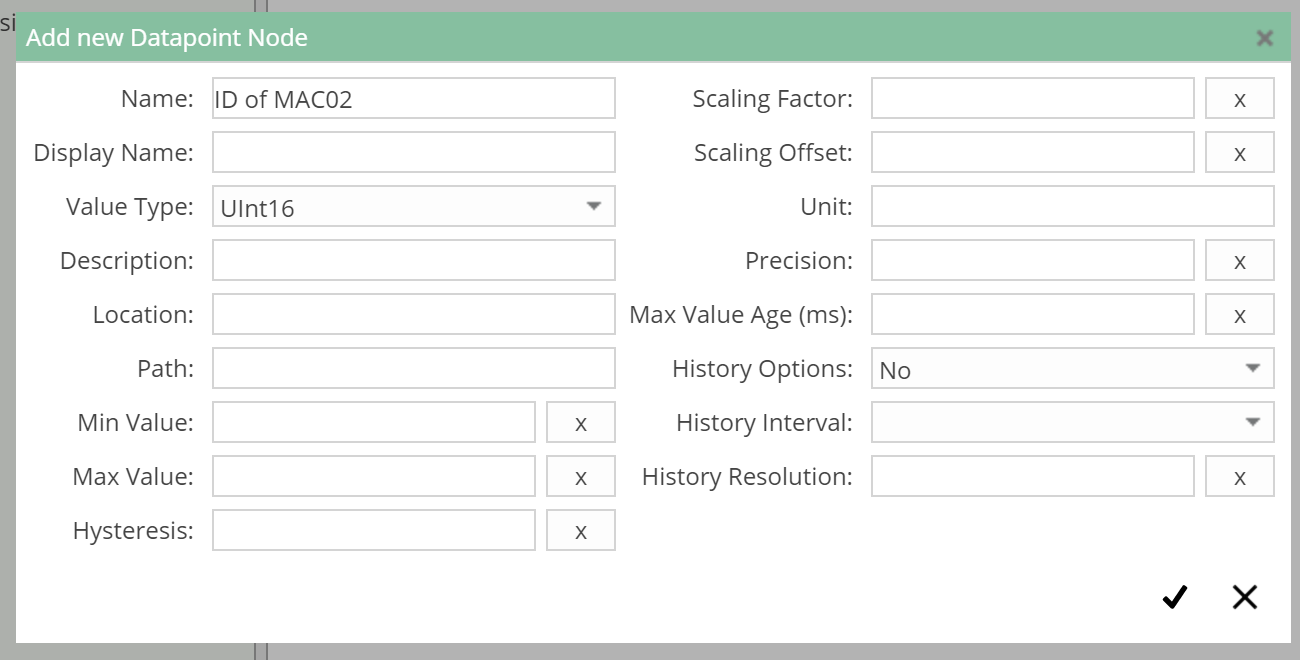
Therefore, first a node of the typeUInt16 is created that will hold this MachineID as constant value:
- Right click on the node
Inputs - Select
Add Datapoint Nodefrom the context menu - In the
Add Datapoint Nodedialog:- Enter
ID of MAC02as the name - Select
UInt16as Value Type
- Right click on the new node
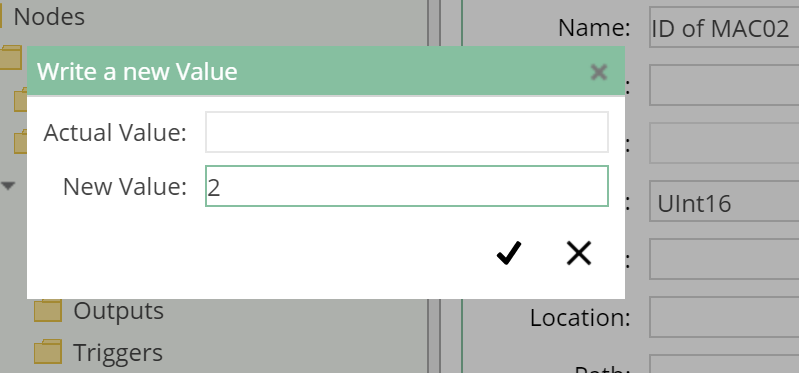
- Select
Write a new Value - In the
Write a new Valuedialog:- Enter the value
2as the new value (as this Transfer will record the data from the machine withMachineID = 2)
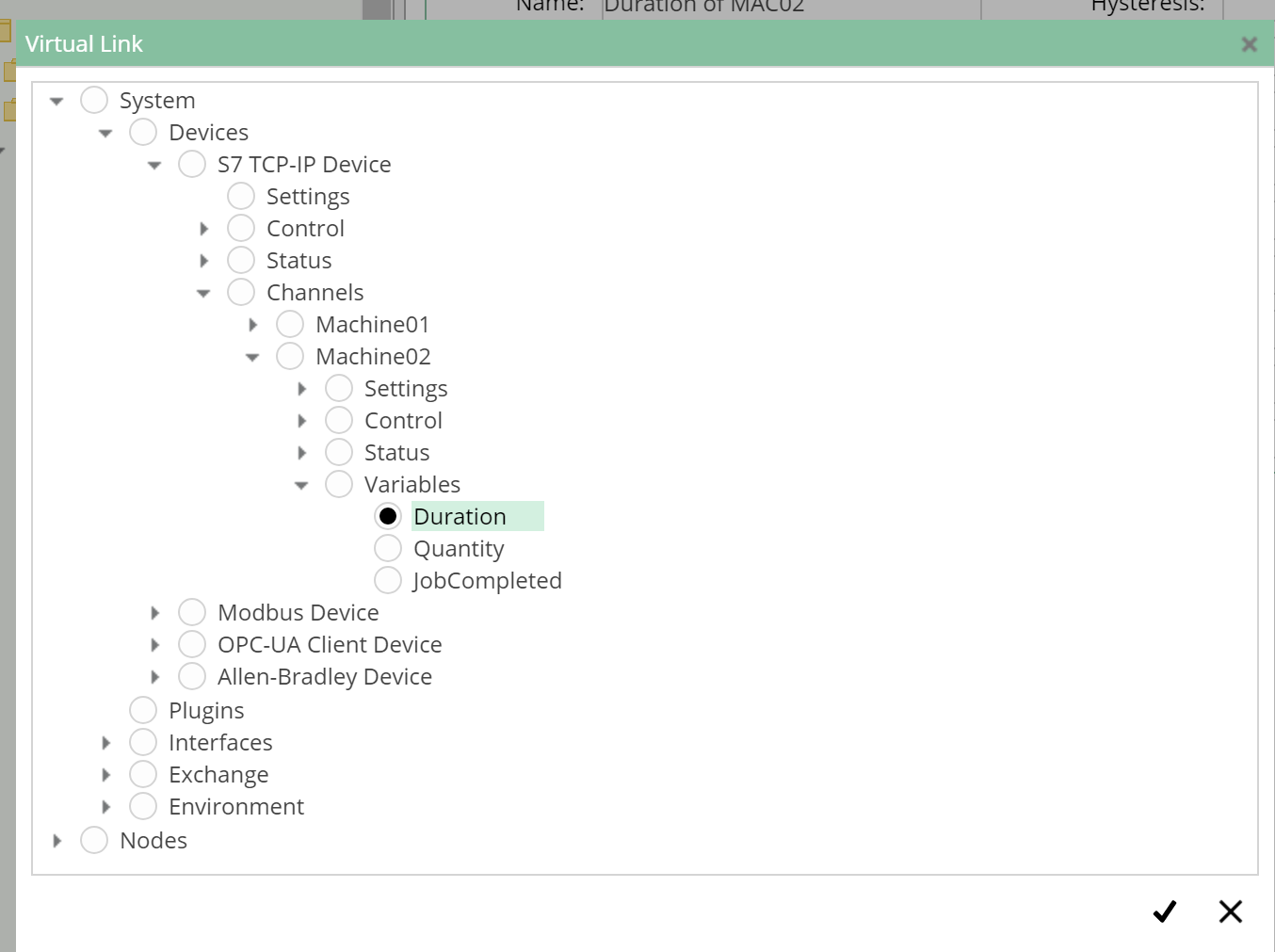
To define the values of the PLC variables as inputs for the transfer, a linked node is created in the Inputs folder whose link target contains the value node that represents the corresponding PLC variable.
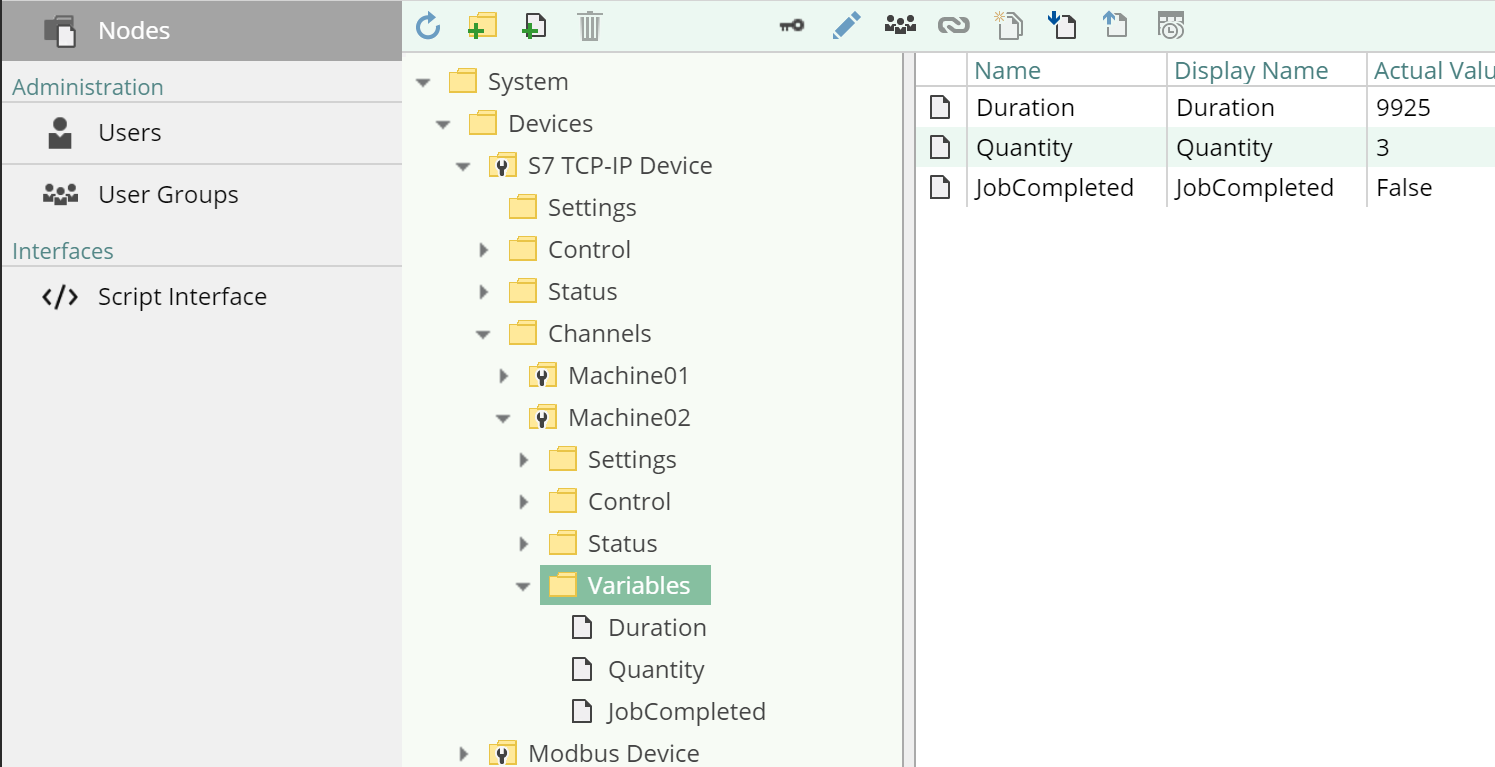
The nodes that represent these variables can be found under the path /System/Devices/S7 TCP-IP Device/Channels/Machine 02/Variables:
For these two nodes, do the following to link them in the Inputs folder:
- Right click on
Inputs - Click on the context menu
Add Datapoint Node - In the
Add Datapoint Nodedialog:- Enter the name of the original node as name (the name of the link node can be freely selected, but in this case it should be obvious which node is the link target)
- Confirm by clicking on

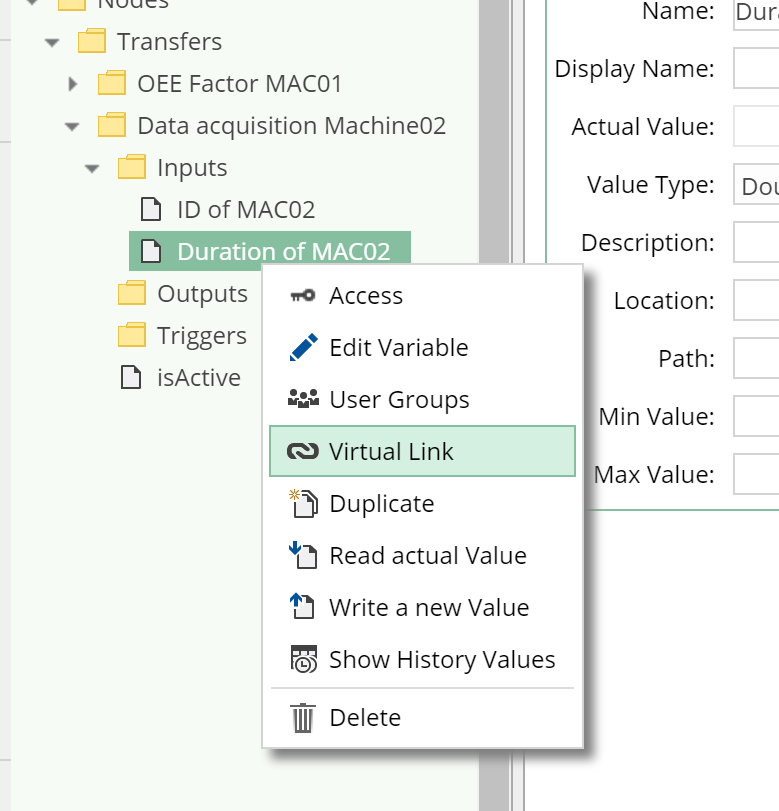
- Right click on the newly created node
- In the
Virtual Linkdialog:- In the opened dialog, navigate to the node to which the virtual link should point
Since the current timestamp shall be saved in addition to the PLC data, a node must me added that delivers this value.
For this purpose Codabix provides a predefined value node, which can be found under the path /System/Environment/DateTime/UtcNow.
When reading this node always the current timestamp is returned.
Now, in the same way as in the previous steps, create another link called Current Timestamp that refers to this node (/System/Environment/DateTime/UtcNow).
2.3 Selection of data targets
Analogously to the sources of the data, the destinations are defined under the folder node Outputs.
The table oeemachinerecord of the database will be used for this.
The nodes that represent the columns of this table are under the path /System/Exchange/SQL Exchange/Databases/OEE/Tables/oeemachinerecord/Columns.
As in the previous step, create link nodes below Outputs that are linked to the following nodes:
- MachineID:
/System/Exchange/SQL Exchange/Databases/OEE/Tables/oeemachinerecord/Columns/MachineID - Duration:
/System/Exchange/SQL Exchange/Databases/OEE/Tables/oeemachinerecord/Columns/Duration - Quantity:
/System/Exchange/SQL Exchange/Databases/OEE/Tables/oeemachinerecord/Columns/Quantity - Timestamp:
/System/Exchange/SQL Exchange/Databases/OEE/Tables/oeemachinerecord/Columns/Timestamp
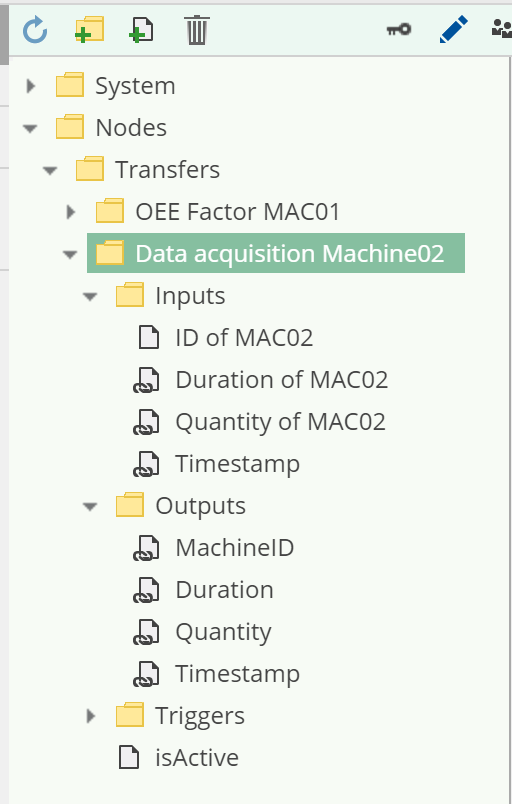
The transfer mechanism uses the order of the input and output nodes to differentiate which data should be written to which node.
The value of the first input node is written to the first output node, the value of the second to the second output node and so on.
You can use drag-and-drop to arrange the nodes under Inputs and Outputs so that their order matches the order in this screenshot:
2.4 Defining the trigger
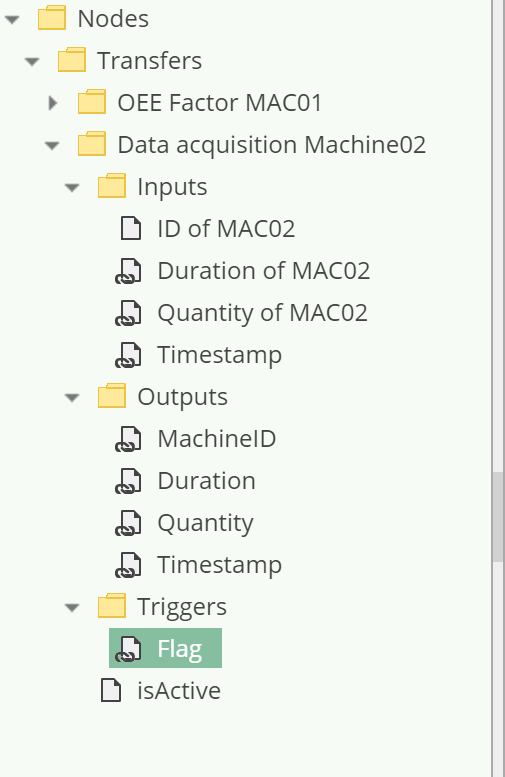
To set up the trigger for our example, create a virtual link under the Triggers folders, whose target is the node /System/Devices/S7 TCP-IP Device/Channels/Machine 01/Variables/JobCompleted.
So the node tree will look like this:
3. Step: Activate and verify functionality
After completing the previous steps, the data acquisition setup is complete.
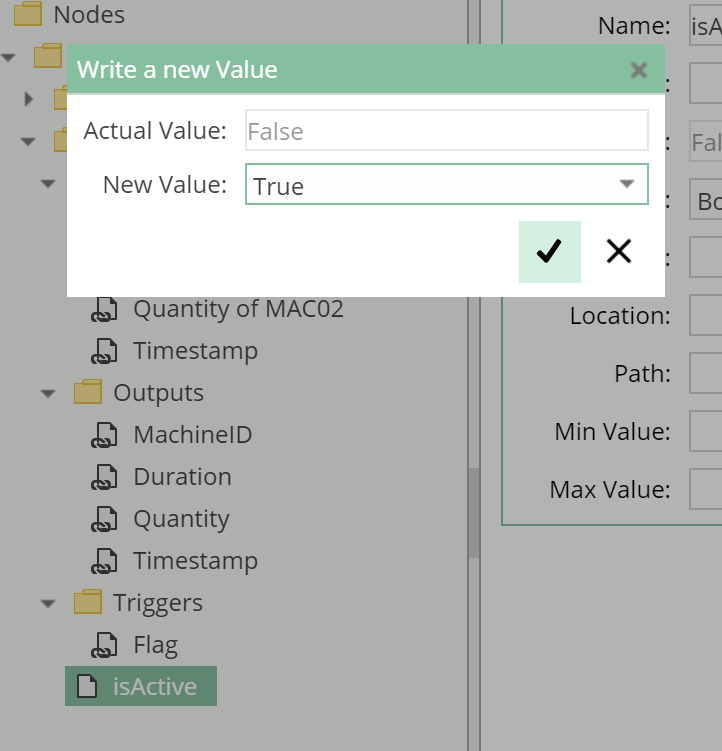
To activate the transfer, the value of the node isActive in the folder of the transfer must me set to true.
To do this, write true as the new node value:
The trigger is now read by Codabix every 500ms and checked for a rising edge.
If this is the case, the inputs are read, then the trigger is reset (the value false is written) and the data is written to the outputs.
This will create a new entry in the database table that contains this data.
The PLC program waits until the trigger has been reset.
After that within 10 seconds new, random values are written to the variables and the trigger is set on true again.
3.1 View in the SQLite browser
You can now verify the functionality using an SQLite browser:
- If you have not already installed an SQLite browser on your system, download the .zip archive that is suitable for your system at https://sqlitebrowser.org/dl/
- Unzip and start the SQLite browser
- Open the database file under the following path
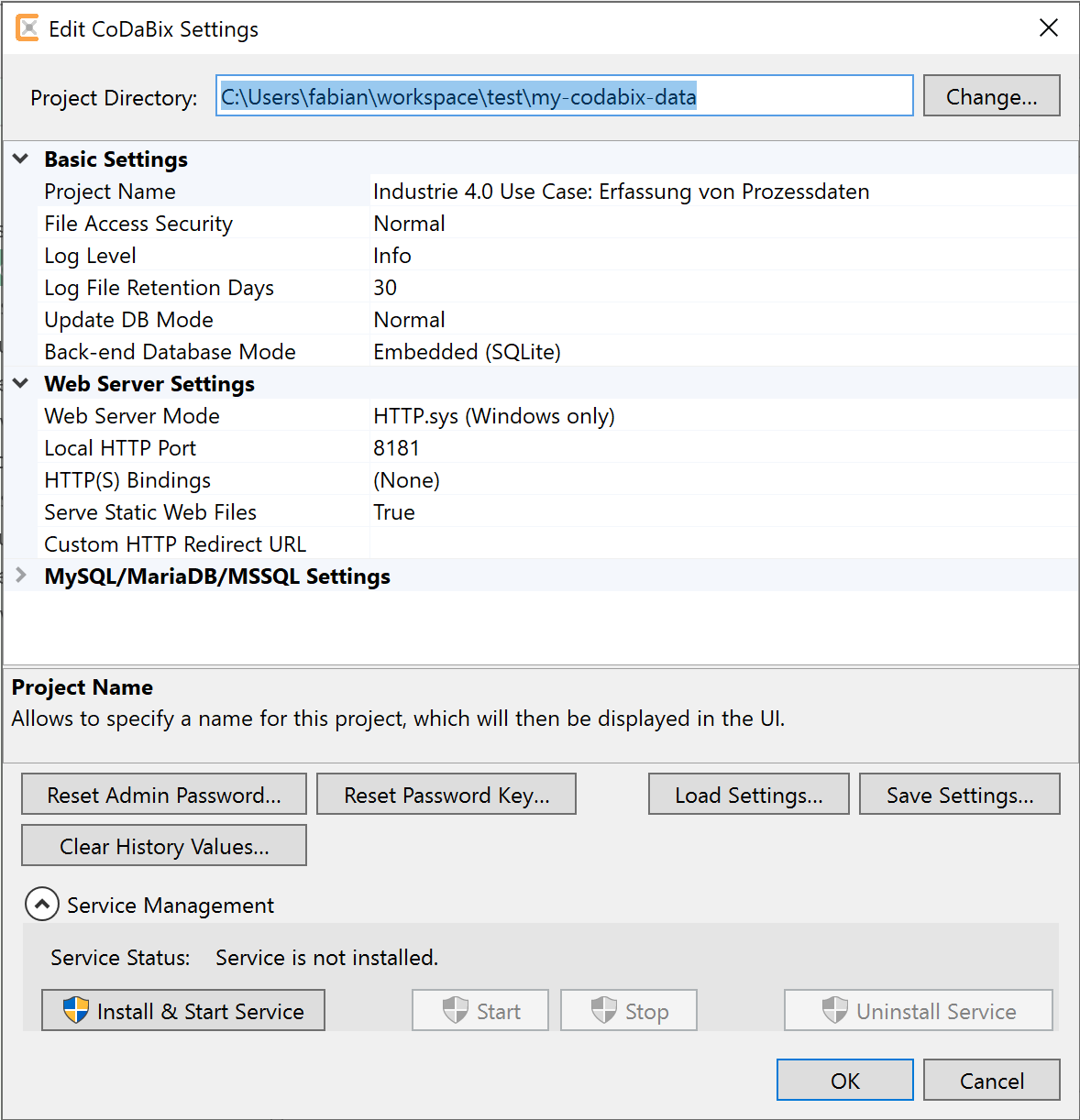
<CodabixProjectDirectory>/userdata/mydata.sqlite.<CodabixProjectDirectory>stands for the path of the project directory on your operating systems filesystem, that you select when you started Codabix for the first time. This path can be fount in the settings dialog:
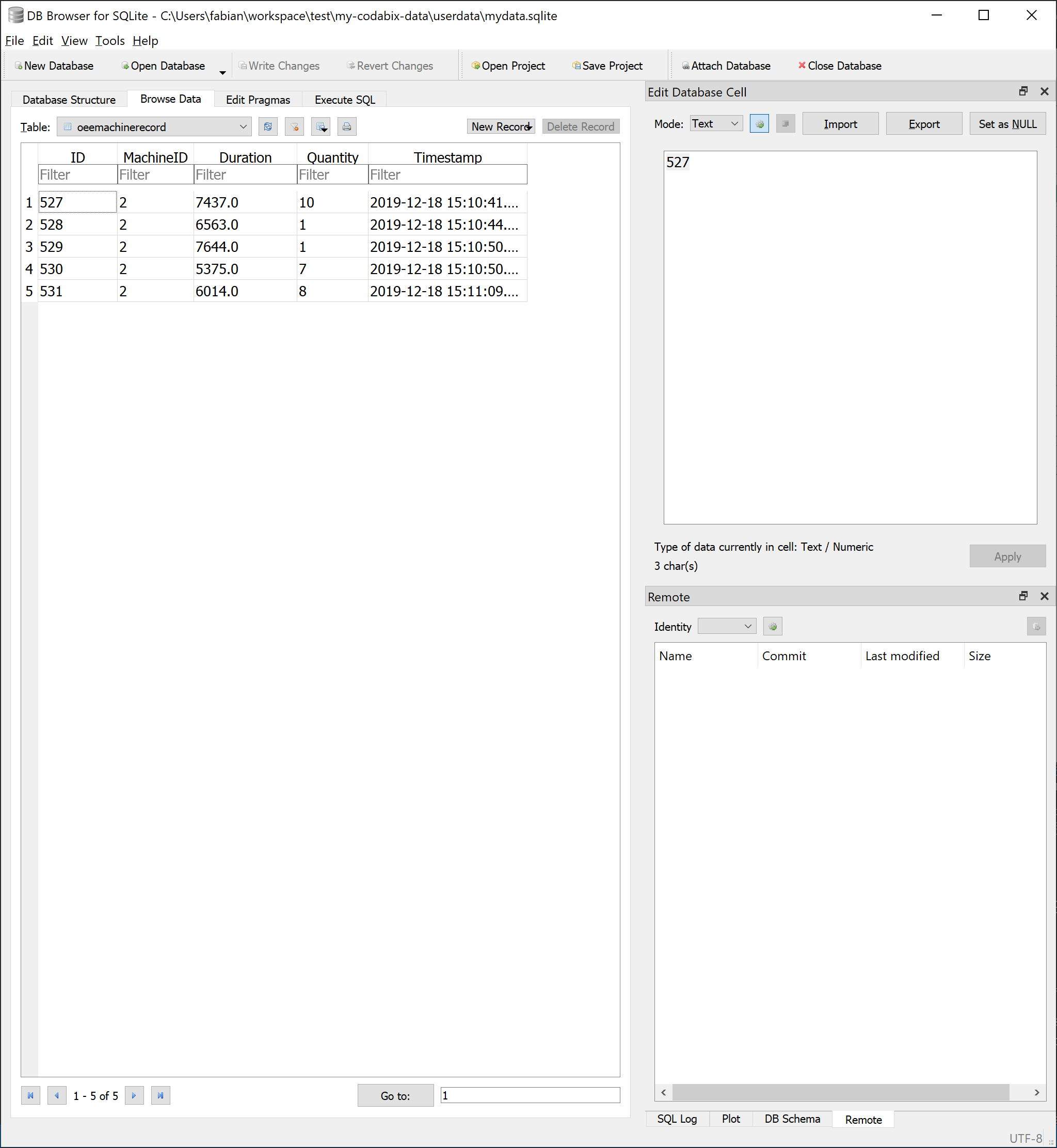
- Open the table
oeemachinerecordin the SQLite browser
- You should now find existing entries there, while new ones are added every 10 seconds
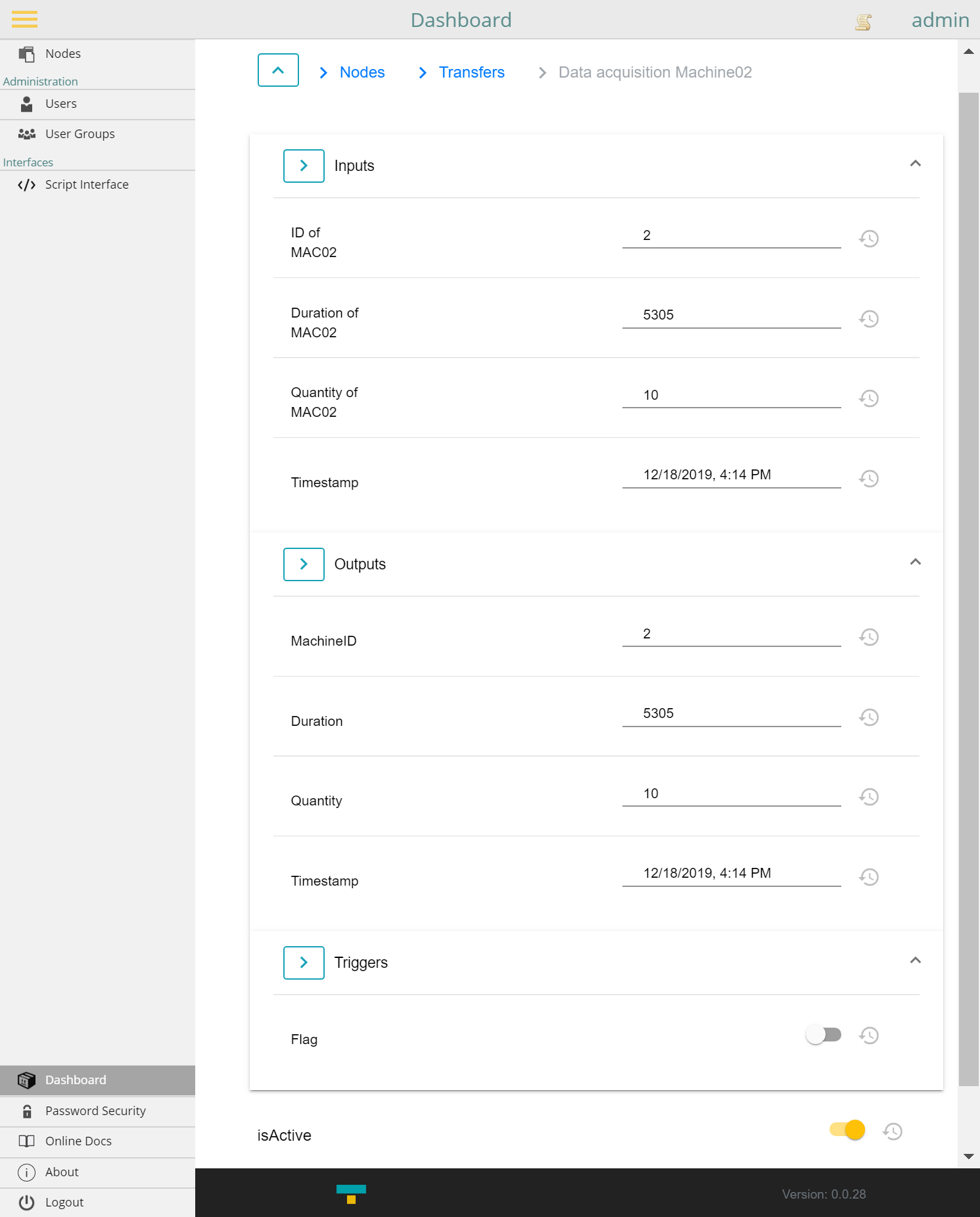
3.2 View in the Codabix dashboard
Another possibility is the view in the dashboard application integrated in Codabix.
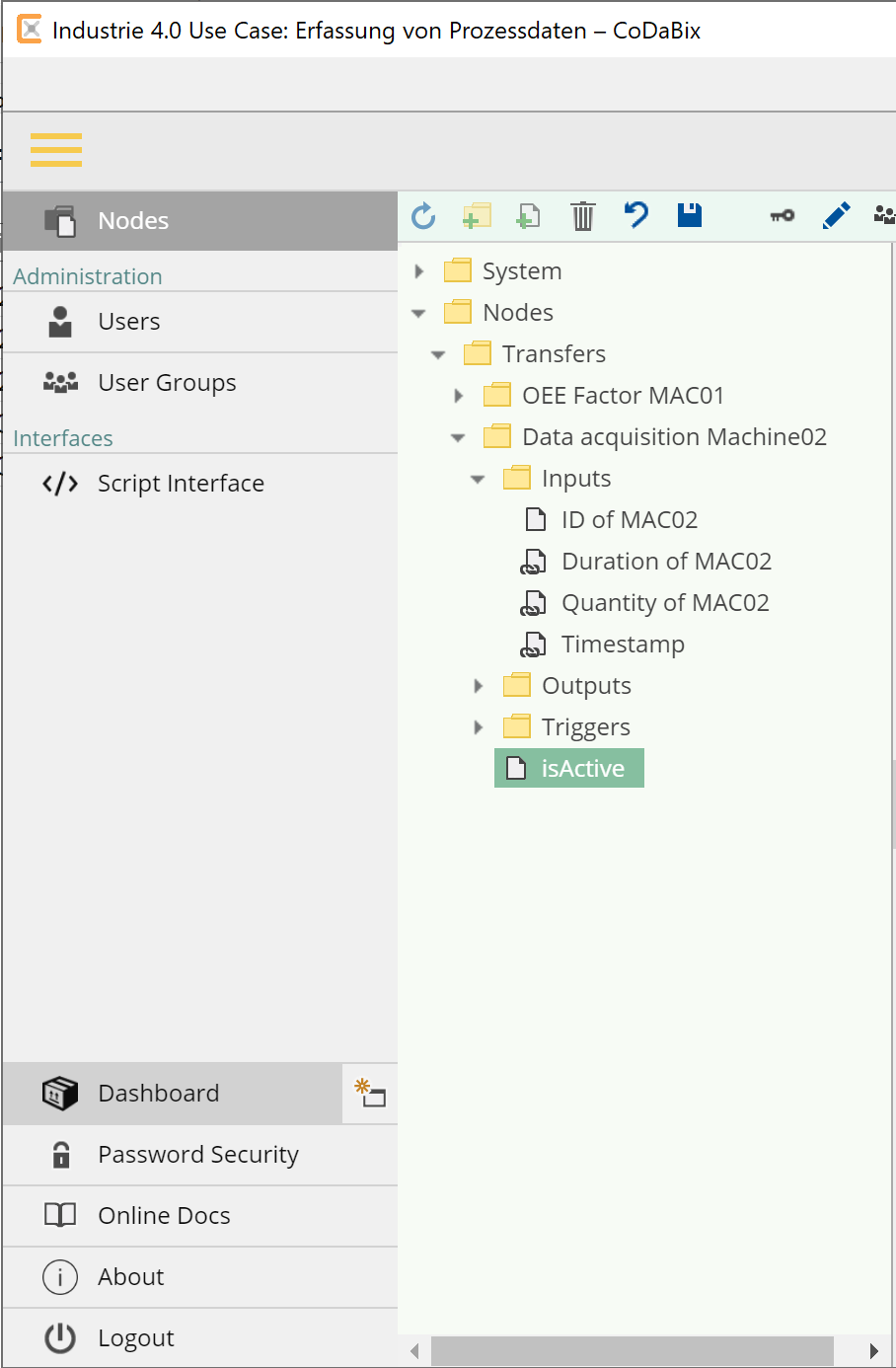
- Navigate to the folder
Data acquisition Machine02 - Expand the three folders
Inputs,OutputsandTriggersby clicking on the symbols next to them
symbols next to them - You can now see the change in the node values in almost real time and can thus observe the triggering and resetting of the trigger and the transfer of data between the inputs ans outputs live: